A guide to business firewalls
Firewalls are your business’s first line of defence against cybersecurity threats. They act as strict border checkpoints, analysing internet traffic to ensure that no unauthorised data enters or leaves your network without your consent.
This perimeter defence extends beyond office networks to encompass your entire Wide Area Network (WAN), safeguarding devices used by remote workers regardless of their location or internet connection.
In this article, we’ll break down what firewalls are, explore their various types, and show you how to implement them effectively to protect your business network.
Contents:
- What is a firewall?
- Types of firewalls for businesses
- Choosing the right firewalls
- Implementing firewalls
- Firewalls as part of your cybersecurity strategy
- Best practices for firewall management
What is a firewall?
Let’s begin with the basics. A firewall can be hardware or software, and its primary function is to act as a “border checkpoint” at key boundaries within your business network, managing the inflow and outflow of data.
Businesses typically deploy firewalls at the boundaries between devices, local networks, wider networks, and the World Wide Web, as illustrated in the diagram below.
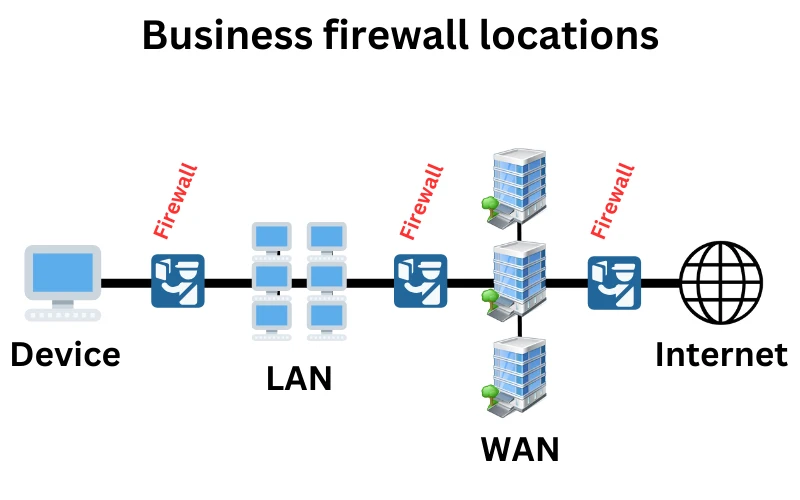
All firewalls operate on predefined rules, allowing authorised data to pass through while blocking or quarantining potentially harmful data. They also enhance privacy by providing features like VPN (Virtual Private Network) and network address translation.
The simplest firewalls filter traffic based on IP addresses (origin), ports (destination), and protocols (type). In contrast, advanced firewalls examine real-time data payloads, detecting malware, suspicious patterns, URLs, or even specific keywords.
Firewalls are continually evolving to address the changing cybersecurity landscape. In the 2010s, advancements focused on mitigating threats like DDoS attacks, phishing, and zero-day vulnerabilities. More recently, the shift to remote work and cloud-based applications has driven the rise of Firewall as a Service.
Types of firewalls for businesses
UK businesses currently use up to four types of firewalls to secure their networks and devices, often simultaneously. Each one operates at a different layer, ensuring security checkpoints at different levels:
- Firewalls-as-a-Service (FWaaS): Cloud-hosted firewalls for remote teams and heavy use of cloud apps.
- Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW): Powerful, stand-alone firewalls that protect business sites (offices, labs, warehouses, etc)
- Software (device) firewalls: In-built firewalls for servers, laptops, and other devices.
- Router-integrated firewalls: In-built firewalls that come by default in standard routers.
Now let’s go into each in more detail:
Firewalls-as-a-Service (FWaaS)
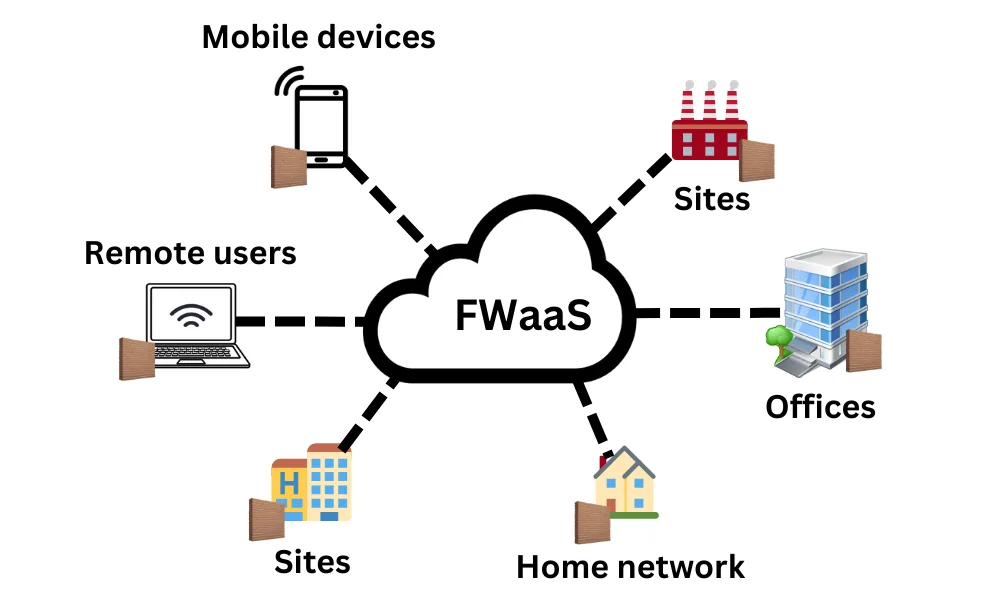
FWaaS is a cloud-based firewall that delivers its firewall services to businesses through an internet connection. It is delivered and managed by third-party providers like Zscaler, Palo Alto Prisma Access, etc. It protects users and devices by controlling and inspecting traffic, regardless of location, using advanced techniques like deep packet inspection (DPI) and application-layer monitoring.
It’s best for global teams, remote-first businesses and cloud applications power users.
Pros
- Scalable, cost-effective, and easy to deploy.
- Offer Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with performance guarantees.
- Fully managed by third parties or easily handled via a single interface.
- Protects business networks and remote work simultaneously.
- Constantly updated against evolving threats.
- Offers advanced threat protection and cybersecurity compliance support.
- Integrates with SASE for comprehensive security.
- The pay-as-you-go model scales with business needs.
Cons
- It may cause latency on slower connections due to bandwidth usage.
- Offers less customisation compared to NGFW.
- Requires trust in a third party for data sovereignty and security.
- Potential migration challenges and risk of vendor lock-in.
Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW)
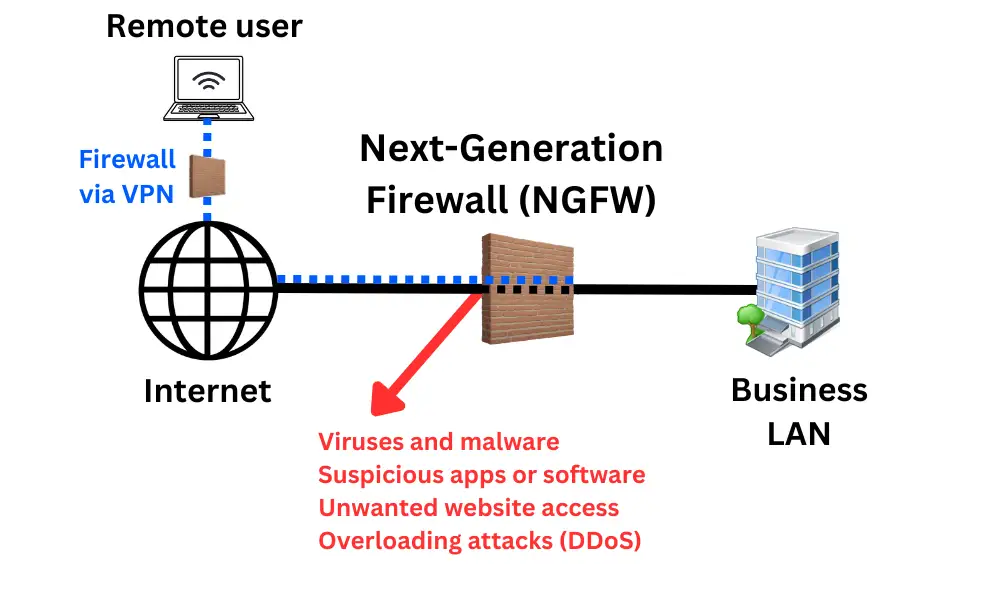
Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW) are advanced hardware-based firewalls installed on-premise. They are highly customisable, offer the most advanced features, and can handle high-capacity connections like leased line broadband, dark fibre and Metro WAN. The setup and management are entirely in the hands of your in-house IT team.
It’s best for protecting on-premise local area networks like offices, universities, schools, call centres, etc.
Pros
- Advanced threat detection (e.g. DPI, IPS) and application-layer control.
- Highly customisable to meet specific business needs.
- Centralised management for on-site and hybrid environments.
- Reduces reliance on external providers by operating locally.
- On-site real-time data inspection with minimal latency.
- NAT adds security by masking internal IP addresses.
Cons
- High upfront costs for hardware and software.
- Requires IT resources for maintenance and updates.
- Limited scalability for growing or distributed businesses.
- Remote workers need VPNs, impacting user experience.
- Prone to misconfigurations without proper management.
- Updates are slower than FWaaS, relying on in-house teams.
Software (device) firewalls
Software firewalls are installed on individual devices, servers, or virtual environments. Once critical, they now serve as an additional checkpoint within your network. They help block insider threats or identify malware before it can spread through your network. Examples include Windows Defender Firewall, pfSense, and AWS Security Groups.
It’s best for providing complementary protection to devices, servers and virtual environments within your network.
Pros
- It is cost-effective (often free) and requires no hardware.
- Flexible deployment on devices, servers, or cloud environments.
- It helps block internal threats and unauthorised traffic.
Cons
- Limited to the device it’s installed on, not network-wide.
- It can impact the performance of devices.
- Effectiveness depends on regular updates and proper management.
- Lacks advanced threat detection features.
Router-integrated firewalls
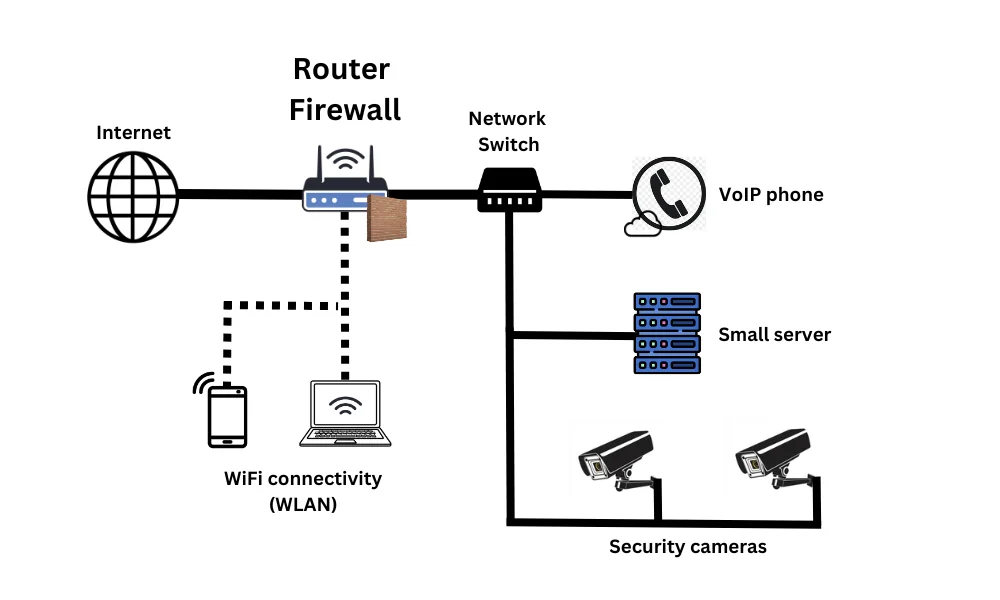
Router-integrated firewalls are built into business broadband routers to provide basic traffic filtering and control. They act as the first and only line of defence for small business networks by blocking unauthorised traffic at the network perimeter. These firewalls are appropriate for small offices, shops, cafes and homes as part of a simple yet effective security setup.
It’s best for protecting small businesses, such as home offices, retail shops, small pubs, and cafes.
Pros
- Combines routing and firewall functionality at no extra cost.
- Simple to set up and manage.
- Offers basic protection against unauthorised access and most threats.
- Does not impact network performance.
Cons
- Lacks advanced features like deep packet analysis and threat detection.
- Unsuitable for complex or large-scale business environments.
- Limited bandwidth and effectiveness depend on proper configuration.
Choosing the right firewalls
Selecting the right type of firewall depends on your business needs, network complexity, and security goals. Here are key factors to consider:
Network size and distribution
Assess the size of your network and whether it spans multiple locations. NGFWs are ideal for centralised, on-premises networks, while FWaaS offers cloud-based security for distributed or remote teams.
Management and expertise
Evaluate your resources and expertise. NGFWs and software firewalls require in-house management and expertise, whereas FWaaS and managed router firewalls can offload this burden to third-party providers.
Scalability requirements
Understand your scalability needs. If your network is growing rapidly, FWaaS offers flexible, pay-as-you-go pricing and seamless scaling, while NGFWs might need significant hardware upgrades.
Level of protection
Consider the level of threat protection you need. NGFWs provide deep packet inspection and advanced threat prevention for high-security environments, while software and router firewalls are suitable for basic or complementary protection.
You can ensure comprehensive and cost-effective protection by aligning your firewall choice with your infrastructure and security priorities.
Business firewalls compared
See the table below to compare firewalls head-to-head and choose the most appropriate for your needs:
| Firewall Solution | FWaaS (Firewall-as-a-Service) | NGFW (Next-Generation Firewall) | Software Firewalls | Router-integrated Firewalls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best for | Distributed teams, remote-first businesses, cloud-heavy environments. | To protect offices and other sites with centralised infrastructure (e.g., servers, PCs, storage). | Complementary device protection. | Home offices, retail shops, small pubs, with basic security needs. |
| Deployment | Cloud-based, no hardware required. | Onsite; Hardware or virtual device. | Software installed on individual devices. | Built into small routers (hardware). |
| Scope of Protection | Entire organisation, regardless of location. | Office network and remote workers connected via VPNs. | Individual devices only. | Small office network. |
| Remote Work | Seamless protection without VPN. | VPN required for secure remote access. | No or minimal benefits. | No or minimal benefits. |
| Security Features | Advanced: DPI, Zero Trust, threat intelligence, user behavior analysis. | Advanced: DPI, IPS, malware detection, application control. | Basic: Monitors and blocks traffic per device. | Basic packet filtering and stateful inspection. |
| Management | Managed by a third-party provider or IT team through the cloud. | Managed by IT team; requires maintenance and updates. | Managed by device admin. | Managed through basic router interface. |
| Performance | Scales easily with cloud infrastructure. | High-performance but requires upgrades. | Dependent on device resources. | Limited by router hardware. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; ideal for global teams. | Scalable but limited to hardware resources. New sites require new hardware. | Not scalable beyond individual devices. | Designed for small-scale use only. |
| Cost | Subscription-based pricing (scalable). | Higher upfront cost for hardware and licenses. | Low-cost or free for standalone use. | Included with router purchase. |
Implementing firewalls
Firewalls are an integral part of network design and implementation, and they should be handled by an experienced IT team or a network service provider (including some business broadband providers). They will ensure your firewalls are set up correctly for your specific context.
Network design
Experts will ideate your network and make a diagram showing all devices and connections, including firewalls, routers, network switches, business VoIP phone systems and other hardware and software components.
They will also include other security measures, such as network segmentation, network load balancing, and business broadband redundancy, to ensure 100% connectivity even during a successful cyberattack.
Deploy the firewall
The firewall will be implemented according to your network setup.
Cloud-based FWaaS requires signing up with a provider, configuring devices and setting security policies.
Hardware Next-Gen Firewalls (NGFWs) require physical installation of the hardware at your network’s perimeter and configuring the rules.
Software firewalls must be installed on individual devices, and basic router firewalls must only be enabled and customised in the router’s admin interface.
Test, monitor, and maintain
Firewalls must be regularly tested to ensure they are working as expected. They can be a recurring IT issue in businesses because they can sometimes be over-secure and reduce necessary access to online resources.
IT teams (or firewall providers) must regularly review logs, update software, and adapt rules as the business evolves.
Firewalls as part of your cybersecurity strategy
Firewalls are the foundation of any business’s cybersecurity but are not a silver bullet. To address all threats, businesses must pair firewalls with complementary solutions.
Examples (to name a few) include segmentation through network switches, VLANs, robust employee training and frequent updates to both software and hardware to mitigate risks effectively.
This section covers how it all ties in:
- Firewalls as a network perimeter defence
- Threats that firewalls protect against
- Threats firewalls don’t protect against
Firewall as a network perimeter defence
Firewalls are to networks what fortified walls with border checkpoints or mobile defence units are to a military defence strategy:
- Perimeter defence: Just as military walls keep enemies out, firewalls block unauthorised traffic and malicious actors from entering the network.
- Inspection points: Like checkpoints that inspect incoming goods or people, firewalls scrutinise data packets, ensuring only legitimate traffic passes through.
- Adaptive defences: Advanced firewalls are akin to intelligent surveillance systems that adapt to evolving threats, such as monitoring activity patterns and responding in real-time.
Threats that firewalls protect against
Advanced firewalls protect against various threats by controlling and inspecting traffic. These include:
- Malware and viruses: Blocking malicious payloads through inspecting incoming traffic.
- Unauthorised Access: Preventing attackers from infiltrating the network.
- Vulnerabilities: Identifying and blocking attempts to exploit software vulnerabilities or weak configurations.
- Phishing and fraudulent sites: Filtering URLs and detecting malicious domains to protect against phishing attacks.
- DDoS Attacks: Mitigating distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks by identifying and throttling suspicious traffic.
- Application-Layer Attacks: Inspecting application traffic to block attacks targeting web services, APIs, or email systems.
Threats firewalls don’t protect against
Firewalls have limitations. They cannot protect you from malicious insiders or social manipulation of your employees. Threats that firewalls alone cannot handle include:
- Insider threats: Employees or contractors misusing their access or leaking sensitive data.
- Phishing: Phishing or scams that trick employees into sharing credentials or sensitive information.
- Zero-day exploits: Advanced attacks exploiting unknown vulnerabilities (unless the firewall integrates with real-time threat intelligence).
- Post-breach activity: Internal network monitoring and response systems are needed once an attacker has bypassed the firewall.
Best practices for firewall management
To maximise the effectiveness of all types of firewalls, follow these general best practices:
- Keep firmware and software updated to protect against the latest vulnerabilities.
- Conduct routine audits of firewall rules, configurations, and logs to identify gaps or misconfiguration.
- Apply strong access controls by limiting access to settings and monitoring user activity for suspicious changes.
- Ensure proper configuration to avoid open ports or unnecessary permissions.
- Use firewalls together strategically, such as router firewalls for basic filtering and NGFW or FWaaS for advanced threat detection.
Firewalls – FAQs
Our business broadband experts answer commonly asked questions on firewalls in UK businesses.
What is application layer filtering?
Application-layer filtering inspects data packets at the application level, allowing firewalls to block specific types of traffic or threats based on their content, not just their source or destination.
Can a firewall prevent ransomware?
While firewalls can block suspicious traffic, they are not a standalone solution against ransomware. Combining them with staff training to prevent phishing, antivirus software to detect device malware, and regular data backups provides significantly stronger protection.
What is NAT?
NAT (Network Address Translation) is a service imparted by advanced firewalls that lets multiple devices within your network share a single public static IP address to communicate with the Internet. It translates each device’s private IP address into the common public address, keeping internal network details hidden from the outside world, including malicious actors.
How much traffic can my router’s firewall secure?
Firewalls built into standard routers are basic but sufficient to secure the traffic volumes of typical broadband connections, including full fibre business broadband.
Providers will provide routers with firewalls designed to match the performance of your connection’s technology.
Whether your business uses SoGEA broadband or business satellite broadband, the router’s firewall should be capable of securing all traffic effectively.
Explore our business broadband deals with the best firewall protection today.

