SD-WAN Explained
The rise of remote work and cloud applications like Microsoft 365 has turned network management into a major challenge for businesses.
How can network admins ensure performance and security for remote employees working on unsecured connections? How can IT teams optimise the performance of cloud-based tools hosted outside the company’s premises?
Enter SD-WAN: a transformative, cloud-based solution that optimises and secures all connections, from office sites to remote devices and cloud apps. In this article, we explain SD-WAN and why it is transforming network management and future-proofing businesses.
Contents:
- What is SD-WAN?
- How does SD-WAN work?
- Key Features of SD-WAN
- SD-WAN use cases
- SD-WAN architecture
- Managed vs Standalone SD-WAN
- SD-WAN functionality
- SD-WAN deployment
- The Future of SD-WAN: AIOps
What is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) is a disruptive, cloud-based software for managing business Wide Area Networks (WANs).
💡 What is a WAN? A closed internet circuit that connects multiple sites like offices, labs, and data centres into a unified network.
It works like a navigation app (e.g., Google Maps) for your business traffic. It continuously monitors the entirety of your network’s pathways and dynamically routes data along the most efficient paths, re-routing traffic when real-time conditions change.
SD-WAN optimises traffic across all WAN connections, from high-performance inter-site Ethernet links to your employees’ home broadband. It’s so pervasive that it even monitors cloud services and optimises connections to cloud apps like UCaaS, Google Workspace and SalesForce.
Its algorithm is smart and will use its understanding of your network to re-distribute traffic along alternative pathways to ease congestion (load balancing) or re-route traffic onto backup connections when a service is down (failover), all while adding a layer of encryption for privacy.
And network admins can manage everything from a single, centralised interface, which greatly eases their workload.
SD-WAN is a paradigm shift in network management, deploying state-of-the-art automation and security to your entire network from the cloud.
SD-WAN vs traditional WAN management
Traditional network management is often fragmented, inefficient, and hardware-intensive. It is static, relying on fixed traffic configurations for routers, switches, and firewalls, which require on-site expertise to set up and modify.
Tasks like connecting new sites or modifying a firewall require substantial time and resources. It struggles to optimise cloud services and cannot adjust to unexpected congestion or outages outside its configured failover and load balancing.
Despite this, many businesses continue with traditional methods. In most cases, this is due to limited familiarity with SD-WAN or because current setups meet present needs. However, SD-WAN is rapidly establishing itself as the go-to solution.
The following table summarises the main differences between a traditional system and SD-WAN:
| SD-WAN | Traditional WAN | |
|---|---|---|
| Setup & Complexity | Centrally managed with minimal manual work. One universal remote for all your routers and switches. | Requires detailed, site-by-site hardware configs, akin to juggling multiple remotes, in different locations. |
| Performance & Reliability | Automatically finds the best path for traffic (just like Google Maps), offering built-in failover. | Depends on fixed routes and manual failover. Like navigating traffic with your AA Road Atlas. |
| Security & Adaptability | Rolls out security policies, encryption and firewalls and any security updates across your entire network at any time. | Relies on separate appliances and static settings, making updates and scaling more cumbersome. |
| Scalability | Makes routing decisions with the routes and devices at its disposal. It adapts to change immediately. | Often locked into expensive MPLS circuits, expanding is slower and pricier. |
| Visibility & Management | Provides a single dashboard for monitoring and analytics. | Relies on multiple, disconnected monitoring tools, each requiring separate checks and configurations. |
How does SD-WAN work?
The key to SD-WAN is that it’s “SD” or “Software-Defined,” meaning one software solution ‘defines’ multiple hardware devices. In this case, SD-WAN controls your network’s routing hardware to optimise traffic by:
Here’s how each element contributes:
1. Gathering network data
SD-WAN deploys agents across your network to monitor performance metrics in real-time:
- Latency: Time taken for data packets to travel between points.
- Packet loss: Percentage of packets dropped during transmission.
- Jitter: Variation in latency, critical for real-time applications like VoIP.
- Bandwidth: Current usage versus capacity.
- External data: Third-party agents or cloud service APIs factor in external conditions like internet outages, provider performance, and cloud services like Microsoft 365.
2. Mapping the network in real-time
The SD-WAN controller uses the collected data to build a real-time map of the network’s state. It evaluates the performance of all network paths and services, including your remote workers’ broadband connections, dedicated links (e.g., dark fibre and MPLS), cloud services like VoIP and Google Workspace, and provider core networks.
3. Routing traffic via APIs
SD-WAN uses APIs to create a virtual overlay network on top of the existing routing hardware like routers, firewalls, and network switches to gain full control. The local configuration of these devices no longer matters as SD-WAN continuously sends its overriding routing instructions based on its understanding of the network and the traffic priorities (QoS) defined by network admins.
Here are some real-world examples of how SD-WAN works in the background to optimise connectivity:
- Call centre: The primary leased line broadband fails during an important sales call. SD-WAN detects the issue and reroutes the call to a failover connection, resulting in only a brief 3-second disruption instead of a call failure, ensuring VoIP call quality.
- Finance: A finance team collaborating on Microsoft 365 to meet a deadline encounters broadband congestion during peak office hours. SD-WAN detects the issue and re-balances the network’s load, diverting low-priority traffic to redundant connections and ensuring uninterrupted productivity.
- Routine backups: An automated, routine backup encounters equipment failure on a wireless leased line link between headquarters and a data centre. SD-WAN re-routes the backup traffic to a secondary satellite business broadband connection, completing the process with only minor delays.
Key features of SD-WAN
SD-WAN has four key features that differentiate it from other solutions:
1. Centralised management
SD-WAN is cloud-based, enabling administrators to configure, monitor, and manage the network from anywhere. This centralised control allows the SD-WAN controller to quickly reroute traffic when its agents detect performance issues, ensuring seamless connectivity and efficiency.
2. Smart routing
There are three smart routing functions used by SD-WAN software:
- Application-aware routing: SD-WAN can prioritise traffic based on its type, sensitivity, and application to guarantee reliability for critical applications like video conferencing, real-time analytics, and e-commerce transactions.
- Dynamic routing: At the same time, SD-WAN supports dynamic routing across multiple connections for load balancing (to avoid congestion at peak times).
- Failover: Turning to a backup connection when the connection fails, selecting paths based on real-time conditions configured with leased line failover solutions.
3. Enhanced cybersecurity
While not envisaged as a cybersecurity software solution, its control of network traffic from the cloud makes it perfect for implementing network-wide security policies, encryption, safe routing, firewalls and zero trust:
- All data traffic routed through SD-WAN gets end-to-end encryption, including remote connections.
- Sensitive traffic can be routed through fully private pathways like dark fibre and leased lines connections, reducing risk.
- Can offer comprehensive Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA ) by integrating into a Secure Access Service Edge (SASE).
- Can integrate with Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS) to offer advanced firewall capabilities across the network.
4. WAN Optimisation
SD-WAN uses techniques like data deduplication, compression, and caching to reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent, leaving bandwidth for other tasks. Here are more details on each technique:
- Data Deduplication: Eliminates redundant copies of data before being sent.
- Compression: Reduces the size of data packets before transmission.
- Caching: Stores frequently accessed data closer to the user.
5. Network monitoring
SD-WAN collects an unprecedented amount of data from across your network, enabling network-wide insights that were once unattainable. With built-in dashboards and analytics tools, network administrators can monitor network performance, identify issues, and optimise operations in real-time.
6. SaaS optimisation
SD-WAN incorporates the availability and performance of cloud-based SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) into its routing algorithm. This ensures optimised connections to tools like Microsoft 365, Google Workspace and SalesForce, regardless of where these are being accessed from, whether from the office, home, or a cafe’s guest WiFi.
7. Service Level Ageements (SLAs)
SD-WAN providers usually offer Service Level Agreements (SLAs) for their services, including uptime, connection latency and Guaranteed Time to Repair (GTTR) and Device Time to Repair (DTTR) for service restoration. The exact terms depend on the type of network, level of redundancy, etc.
8. Network-wide compliance
Some advanced SD-WAN products include in-built compliance functionality that ensures adherence to industry standards like GDPR and HIPAA across your entire network. It will flag your administrators when your setup conflicts with specific regulations.
SD-WAN use cases
As the latest technology for network management, SD-WAN can improve any business’s wide area network, regardless of size or sector.
Generally, the more complex the network (i.e., the more connections and devices it manages simultaneously), the more useful SD-WAN becomes.
This makes it particularly beneficial for:
- Multi-site businesses: Retail chains, banks, and other distributed organisations.
- Cloud-centric businesses: Businesses migrating workloads to SaaS or public cloud gain more efficient, application-aware routing and faster cloud access.
- Remote workforces: SD-WAN improves connectivity for distributed teams regardless of their connection technology (e.g., fibre optics, mobile business broadband, Starlink, etc.).
- Cybersecurity compliance: Industries like healthcare and finance use SD-WAN to enforce security policies globally and meet strict regulatory requirements.
- Disaster Recovery & Redundancy: Multiple active connections (e.g., MPLS, broadband, 5G business broadband) enable seamless failover and business continuity.
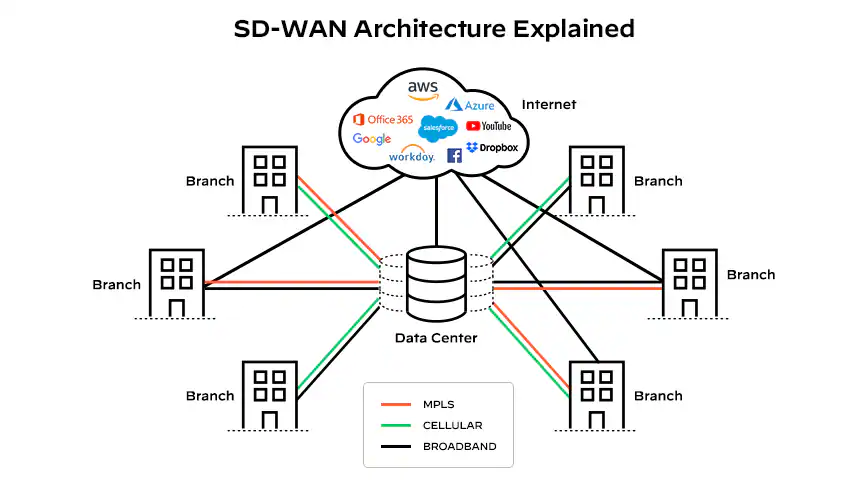
SD-WAN architecture
The most conventional approach is to use SD-WAN hosted from the cloud, but some businesses require other SD-WAN setups to address niche use cases. There are three distinct SD-WAN architectures to choose from:
- Cloud-based SD-WAN: The most common and convenient implementation, where a provider handles hosting, troubleshooting and updates in its cloud while your business handles implementation and configuration. It’s the best for businesses relying on cloud applications like remote VoIP solutions.
- On-premise SD-WAN: Offers greater control and may be necessary for businesses with strict compliance requirements or those needing high-performance local access for internal applications.
- Hybrid SD-WAN: A mix of both. Most on-premise implementations also have a cloud-based component for their SaaS and remote or hybrid workers.
SD-WAN management
Businesses can manage their SD-WAN through their in-house IT team or partner with a specialised managed service provider. Each approach has distinct benefits and trade-offs, depending on your organisation’s needs:
Managed SD-WAN
A provider handles deployment, configuration, and operations, offering ease, expertise, 24/7 support, and SLAs. It’s ideal for businesses with limited IT resources but is more expensive and provides less direct control. However, it can be cost-effective when bundled with VoIP phone systems, leased lines, and dark fibre.
Self-managed SD-WAN
The business oversees all deployment and management aspects, giving it full control and potential cost savings. However, maintaining it requires significant in-house expertise and ongoing effort. While it’s less costly on its own, your business must bear the operational costs of staff.
SD-WAN functionality
Like other software solutions, you can often choose between something like “Basic” and “Pro” versions of SD-WAN, depending on your required functionality. Here is what you will usually get for each:
Core SD-WAN functionality
- Optimised routing: Application-aware routing and dynamic path selection for load balancing and failover.
- Network monitoring: Dashboards and analytics to gain visibility into network performance.
- Centralised management: A single dashboard for configuring and monitoring the network.
- WAN security: Built-in encryption and other security features.
- WAN optimisation: Accelerates application performance and reduces data transfer overhead.
Advanced SD-WAN functionality
- Cloud services integration: Direct connections to any SaaS you use, such as small business VoIP and CRMs.
- Advanced security: Additional security through Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS) integration.
- Compliance tools: Additional tools tailored to ensure adherence to industry standards like GDPR, PCI DSS, or HIPAA.
SD-WAN deployment
Deploying SD-WAN involves a structured, often challenging process. Without going into detail, here is an overview summary of the process:
- Plan: Audit your current WAN connections and infrastructure, then define your business and technical objectives. Choose a suitable provider, and decide how SD-WAN will coexist with or replace parts of your legacy network.
- Design: Outline the network architecture, emphasising traffic priorities and security policies. Plan how SD-WAN will interact with existing MPLS or other services, including cloud or data centre requirements. Anticipate integration needs for routing and security across both new and legacy environments.
- Pilot: Test the SD-WAN solution at a small number of sites. Verify performance, confirm that integration with existing systems or services meets your objectives, and refine configurations based on real-world metrics such as latency, jitter, and bandwidth utilisation.
- Rollout: Gradually expand deployment or integrate SD-WAN across all sites and connections while monitoring user experience and security. Make policy adjustments to ensure optimal traffic flow and minimal disruption as each location comes online.
- Optimisation: Use centralised orchestration to manage ongoing updates, expansions, and performance improvements. Continuously monitor key metrics, revisit policies, and adapt QoS (Quality of Service) or security settings to meet evolving business demands and application requirements.
Deployment challenges
Despite the many benefits of SD-WAN, its deployment/integration often presents unique challenges, most commonly:
1. Handling existing links
Integrating SD-WAN with existing Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) or legacy networks can be tricky, especially in large enterprises that manage multiple vendor solutions. This usually occurs when organisations migrate to SD-WAN or during company mergers/acquisitions, where each party has its unique network vendors and solutions.
3. Addressing skill gaps
Adopting SD-WAN demands specialised knowledge of cloud environments, virtualisation, network orchestration, and cybersecurity threats. This is especially problematic for SMEs (Small and Medium Enterprises) with limited expertise trying to maintain complex SD-WAN deployments.
These challenges can often be overcome with assistance from managed SD-WAN solutions.
The future of SD-WAN: AIOps
SD-WAN is closely intertwined with the rise of Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations (AIOps), which promises significant improvements in network agility, automation, and insight. Essentially, SD-WAN is due to become significantly more efficient, cheap, scalable, and user-friendly.
AiOps will enhance SD-WAN as follows:
- Proactive management: Using predictive analytics to identify potential issues before they even occur. For SD-WAN, this means detecting performance degradations, predicting bandwidth constraints, and preemptively rerouting traffic to maintain seamless operations.
- Improved security: AIOps will bolster SD-WAN security by detecting real-time anomalies and potential threats. Its machine learning models evolve with new patterns, enabling rapid responses to emerging cybersecurity threats.
- Actionable Insights: AIOps will provide detailed insights into network health, application usage, and overall performance, providing insights for data-driven decisions and fine-tuning SD-WAN configurations for optimal outcomes.
SD-WAN – FAQs
Our business broadband experts answer commonly asked questions on SD-WAN:
How does SD-WAN benefit hybrid work?
SD-WAN benefits hybrid work by providing equally secure and reliable connectivity for remote and on-site employees. Employees receive in-built optimised connectivity and encryption when your business adopts an SD-WAN that supports their temporary connectivity.
How does SD-WAN benefit IoT?
SD-WAN makes IoT easier to manage and more scalable, providing better connectivity and security. It lets IT staff manage all devices from one platform. Devices can be added or removed remotely, and their data routing will be optimised and automatically secured.
How is SD-WAN different from VPN?
SD-WAN is a comprehensive network management solution that optimises and secures entire networks, while VPN is simply a tool for creating secure point-to-point connections.
How is SD-WAN different from SASE?
SD-WAN is a sub-component of SASE (Secure Access Service Edge). SASE combines SD-WAN’s network optimisation with comprehensive cybersecurity services, such as secure web gateways, zero-trust network access and cloud access security brokers. It’s the unified, cloud-native solution for networking and security.

