Dynamic IP Addresses
Dynamic IP addresses provide businesses with temporary IPs that change periodically.
While they pose no issues for most business applications, workarounds are required for self-hosting, multi-site connectivity, and IP-based authentication.
This article dives into dynamic IP addresses, explaining why they are needed, how they work, and how to address the challenges they introduce in business networks.
Contents:
- What is a dynamic IP address?
- How do dynamic IPs work?
- Why are dynamic IP addresses necessary?
- Impact of dynamic IP addresses on businesses
What is a dynamic IP address?
A dynamic IP address is a type of public IPv4 address assigned by default to most fixed line business broadband connections in the UK.
It is called “dynamic” because it changes periodically based on the provider’s IPv4 availability and lease durations. This differs from a “static” IP address, which remains fixed but must be requested separately, and at an additional cost.
Dynamic IP addresses are assigned to business broadband routers, meaning that all devices and services connecting to the internet via the router inherit the changing IP address.
For most online activities like browsing, video conferencing, and accessing cloud applications, dynamic IPs have no impact. However, they can cause issues for self-hosting, site-to-site VPN connections and IP-based authentication, for which workarounds are required.
Dynamic IPs are necessary to efficiently manage the limited supply of IPv4 addresses available to providers to assign to its subscribers.
What is an IP address?
If you already know, skip to the next section.
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique numerical identifier assigned to a device within a network. It acts as an identifier and a locator, enabling devices to communicate over the internet.
How do dynamic IPs work?
Dynamic IP addresses rely on two key technologies to ensure that each broadband subscriber always has a unique and valid IP address:
1. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
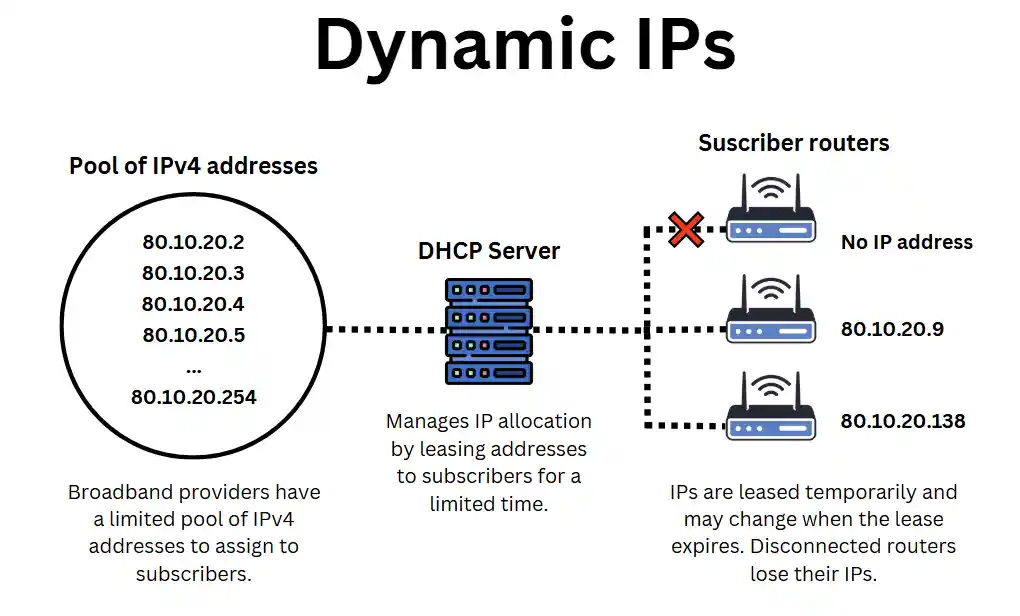
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is the foundational technology that allows providers to manage their pool of IPv4 addresses. The protocol runs continuously on the provider’s servers, automatically assigning and managing IPs.
When a subscriber’s router or modem connects to the provider’s network, it requests an IP address. The DHCP server assigns a public IPv4 address from the provider’s available pool and “leases it” to the router for a set period.
The router keeps the assigned IP unless one of the following occurs:
- The lease expires: The DHCP server checks availability. If demand is low, the lease may be extended, allowing the router to retain the same IP. Otherwise, a new IP is assigned.
- Providers reallocate addresses: The provider may reshuffle IP assignments before a lease expires to optimise network performance, manage congestion, or free up unused addresses.
- The router disconnects: If it is turned off or rebooted, it must request a new IP upon reconnection. Depending on availability, the DHCP server may assign the same IP or issue a different one.
While DHCP ensures that your router always has a valid IPv4 address to communicate externally, another technology is required to assign unique IPs to devices within your local area network.
This brings us to Network Address Translation (NAT).
2. Network Address Translation (NAT)
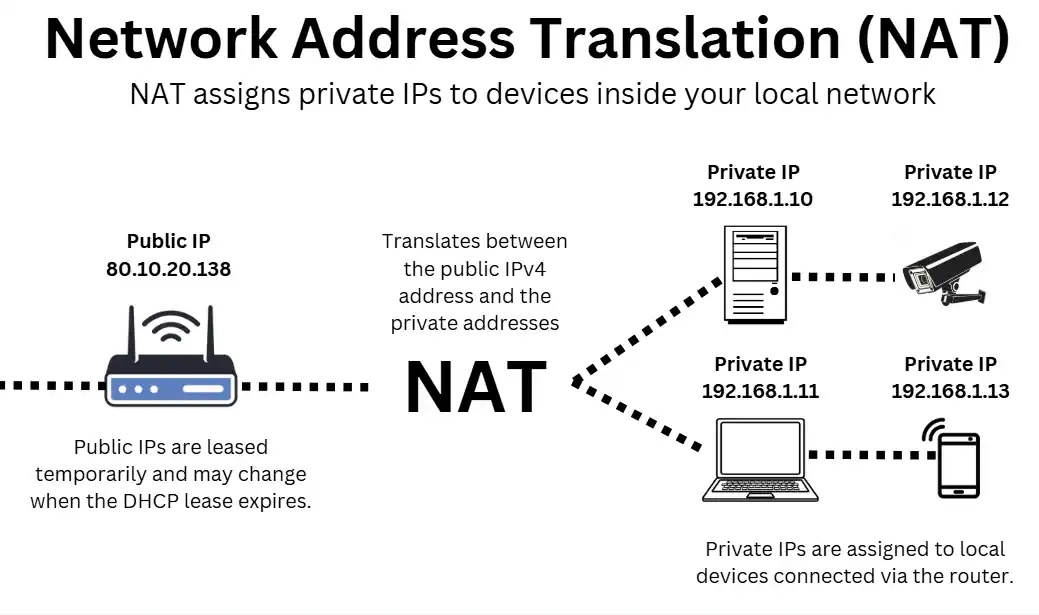
Every device within a local network (e.g., servers, laptops, tablets, VoIP phones) requires its own unique IP address to function properly.
Since there aren’t enough IPv4 addresses to give each device a public IP, providers use Network Address Translation (NAT), which is a function built into broadband routers.
NAT assigns connected devices with private IP addresses, allowing them to communicate internally while sharing a single public IPv4 address for external communication.
For example, if your router is assigned the public IPv4 address 203.0.113.45, NAT assigns private IPs to devices inside your local network:
- Laptop: 192.168.1.10
- VoIP phone: 192.168.1.20
- Server: 192.168.1.30
When these devices connect to the internet, NAT translates their private IPs into the router’s public IPv4 address, allowing them to communicate independently with any external service, such as VoIP, UCaaS, cloud storage, and web applications.
In summary, this system ensures seamless connectivity for every device while conserving the limited pool of IPv4 addresses available to your provider. It’s a win-win situation.
Why are dynamic IP addresses necessary?
Dynamic IP addresses are essential for UK businesses because the world still relies heavily on IPv4 addressing, which only supports approximately 4.3 billion unique IP addresses by design.
This limited supply requires a strict global allocation system managed by Regional Internet Registries (RIRs). These organisations distribute blocks of IP addresses to broadband providers, governments, and large corporations worldwide.
In the UK, this responsibility falls to RIPE NCC (Réseaux IP Européens Network Coordination Centre), which allocates IPv4 addresses to business broadband providers, leaving them with a limited supply.
In most cases, providers receive fewer IP addresses than they have subscribers. However, they can still ensure that each customer has a unique and valid IP address thanks to dynamic IP addressing, which efficiently manages their limited IPv4 addresses.
Note: Dynamic IP addressing applies only to fixed line broadband connections (e.g., full fibre business broadband, SoGEA, and leased line broadband). Wireless broadband technologies like business mobile broadband, Starlink and OneWeb rely on CGNAT technology. Read more about CGNAT here.
Impact of dynamic IP addresses on businesses
Unfortunately, workarounds usually have impacts down the line. While dynamic IP addresses help extend the lifespan of ageing IPv4 technology, they introduce challenges for certain business applications, including self-hosting, security, and inter-site communication.
Let’s explore these issues and the solutions businesses can implement:
- Self-hosting difficulties
- IP-based authentication issues
- Business WAN problems
- SIP stability issues in business VoIP
Self-hosting difficulties
Solution: Dynamic DNS (DDNS) or static IPs
Many small businesses and enterprises prefer to self-host services such as website hosting, intranet portals, and VPNs rather than relying on third-party providers. This approach offers greater control and privacy over data and applications.
However, self-hosting with a dynamic IP requires an additional workaround. Each time the router’s IP address changes, DNS records become outdated, causing external users and services to lose access.
This leaves businesses with two options:
- Pay for a premium static IP, which bypasses the problem entirely by ensuring the IP address never changes. However, static IPs come at an additional cost and are not included in all business broadband contracts.
- Use Dynamic DNS (DDNS), automatically updating DNS records when the IP changes, ensuring uninterrupted access. Many third-party providers offer free or low-cost DDNS services, making this a common solution for home-based businesses and cases where a static IP is unavailable, like in small business broadband.
When combined with broadband redundancy, load balancing, and leased line failover strategies, both DDNS and static IPs allow businesses to successfully self-host services without disruption.
IP-based authentication issues
Solution: Third-party VPNs, Identity-based authentication, Dynamic DNS (DDNS)
Many businesses still use IP-based authentication to control access to firewalls, APIs, SaaS platforms, payment gateways, and cloud services by whitelisting specific trusted IP addresses.
However, this method is incompatible with dynamic IPs without the appropriate workarounds, as each time the IP changes, access would be lost. Businesses relying on IP-based security need to implement one of the following solutions:
- Use a third-party VPN: Businesses can route traffic through a third-party VPN provider with a dedicated static IP.
- Switch to identity-based authentication: Most modern security frameworks no longer rely on IP whitelisting. Businesses should transition to OAuth, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), Single Sign-On (SSO), or Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) for greater security and flexibility.
Business WAN issues
Solution: Business SD-WAN solutions, Dynamic DNS (DDNS), Cloud VPNs
Multi-site businesses often rely on business Ethernet technologies to establish high-performance, always-on connectivity between their key locations.
When dedicated connections like MPLS or dark fibre are unavailable, businesses must use site-to-site VPNs to connect offices. However, these VPNs would be unreliable if relying on IT staff manually updating VPN settings with constantly changing IPs, especially across multiple sites.
Workarounds for this issue include:
- Using SD-WAN: SD-WAN solutions automatically detect IP changes and reroute traffic, ensuring seamless connectivity without manual intervention. It’s the go-to software to manage business WANs as it adds security, resilience, and route optimisation.
- Configuring site-to-site VPNs with DDNS: Instead of relying on static IPs, VPNs can use DDNS hostnames, ensuring they always connect to the correct IP address.
- Move to cloud-based VPNs: Businesses can reduce reliance on IP-based VPNs by adopting IP-agnostic cloud-based VPNs that do not depend on static addresses.
SIP stability issues in self-hosted VoIP
Solution: Static IPs, Dynamic DNS (DDNS), Session Border Controllers (SBCs), NAT configuration
Businesses VoIP phone systems rely on SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) to manage voice calls over the internet. These systems require consistent IP addresses to maintain stable connections with SIP servers and ensure smooth communication.
With dynamic IPs, frequent IP changes cause registration failures, dropped calls, and one-way audio issues, especially if firewalls or SIP providers rely on whitelisted IPs for authentication.
Workarounds for this issue include:
- Using a static IP: Ensures any VoIP system (incl. small business VoIP and additional VoIP features) always connects from the same external IP, preventing registration and VoIP call quality issues.
- Implementing DDNS: Allows SIP servers to track changing IP addresses and reroute calls accordingly.
- Deploying a Session Border Controller (SBC): Acts as an intermediary between the internal local network and the SIP provider, managing NAT traversal and improving security.
- Configuring NAT correctly: Firewalls and business broadband routers should be SIP-aware to prevent issues with packet routing and call negotiation.
Note: This impact is technically an extension of self-hosting using dynamic IPs, but warrants its own section because many organisations have expressed their willingness to host their own VoIP for cybersecurity compliance.
Dynamic IPs – FAQs
Our business broadband experts answer commonly asked queries regarding dynamic IP addresses used by UK businesses:
What is the difference between a static IP and dynamic IP address?
Dynamic IP addresses mean that your provider will regularly change your business’s IP address, while a static IP means you get to keep the same IP address during your broadband contract duration.
Dynamic IP addresses are the default for all residential and business broadband connections because they enable providers to continue offering broadband services with IPv4 technology without having to overhaul their networks to support IPv6 just yet.
This leaves static IP addresses as a premium option for businesses that need to self-host VPNs, apps, e-mails, websites, etc.
Static IP addresses typically raise business broadband prices. Find the best prices today using our compare business broadband deals service.
How does my business obtain a dynamic IP address?
Business broadband providers assign dynamic IPs by default, using DHCP, requiring no user action. To ensure a device or router receives one, network settings should be set to “obtain an IP address automatically.”
Dynamic IPs means your IP will periodically change due to re-assignments and router reboots/disconnections. Businesses that need a fixed address for self-hosting or IP-based authentication should consider a static IP or dynamic DNS.
Are dynamic IPs extra secure?
There are some inadvertent cybersecurity benefits to using dynamic IP addresses. Since the IP changes periodically, it reduces the risk of targeted attacks, advanced persistent threats, and unauthorised access attempts. Malicious actors will find it marginally harder to launch long-term exploits against a system that frequently changes its IP.
However, dynamic IPs are not a substitute for cybersecurity essentials. Businesses should still implement firewalls, VPNs, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and encryption to protect their networks.
Does 5G and satellite broadband also rely on dynamic IP addresses?
No. 5G business broadband and business satellite broadband use Carrier-Grade NAT (CGNAT) to manage IPv4 address limitations.
CGNAT assigns private IPs to subscribers, allowing multiple users to share a single public IPv4 address, similar to NAT in fixed line broadband. This eliminates traditional dynamic IP concerns, as users don’t receive a unique public IP.

