What is cable broadband?
Full fibre broadband is transforming internet speeds across the UK, but it’s still out of reach for many households and businesses. In locations without full fibre, Virgin Media’s cable network can offer the only option for gigabit-speed broadband.
Virgin’s cable broadband is available to over 16 million properties in Britain, providing speeds of up to 1,100Mbps.
This guide explains Virgin Media’s alternative approach to delivering ultrafast broadband using its cable broadband network. Here’s what we cover:
- Virgin’s cable broadband service
- How does cable broadband work?
- Cable broadband vs other broadband types
- Cable broadband plans and speed tiers
- Cable broadband coverage and availability
- Advantages and disadvantages of cable broadband
Virgin’s cable broadband service
Cable broadband is a part-fibre broadband connection that combines fibre-optic and coaxial cables to deliver high-speed internet.
Coaxial cables are a type of electrical cable specifically designed to carry high frequency signals with minimal interference, ideally suited for Virgin’s TV and internet services.
These cables operate across a high-frequency range and are protected by robust shielding, enabling fast and reliable speeds. The coaxial cables can support speeds up to 10 times faster than an equivalent SoGEA broadband connection, which uses a copper telephone cable for the final mile.
A cable business broadband connection can deliver gigabit internet speeds with performance comparable to top full fibre packages offered by providers like BT business broadband, which utilise the Openreach network.
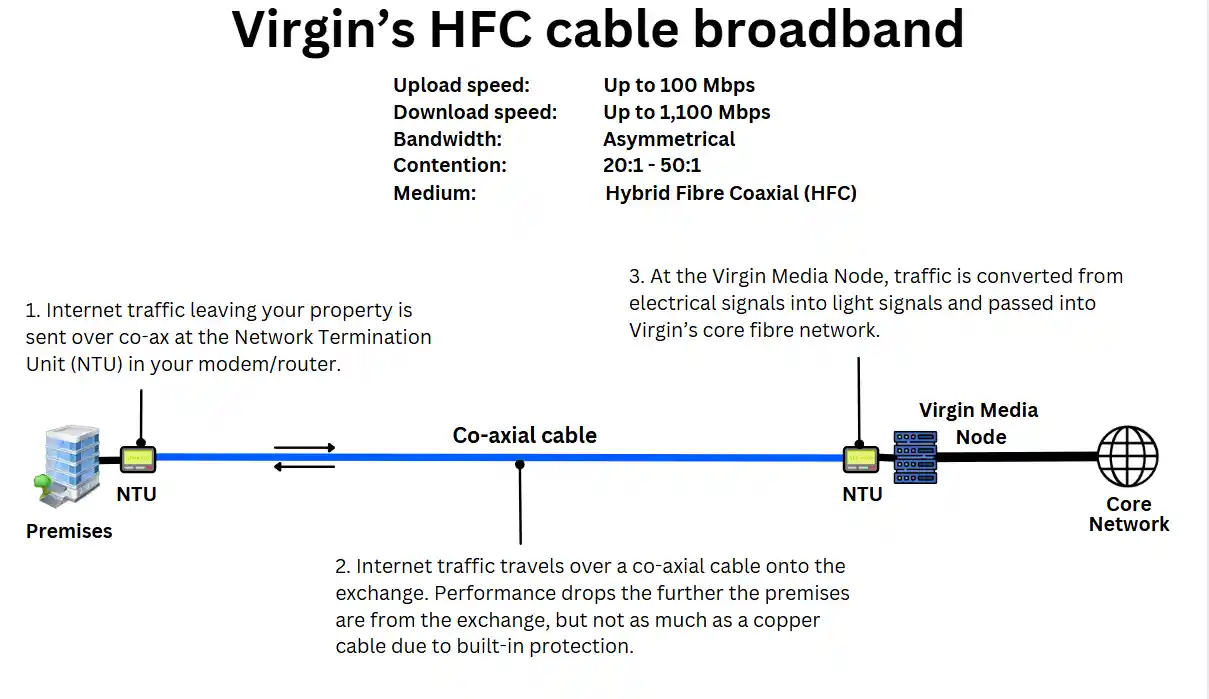
How does cable broadband work?
Virgin Media delivers its cable broadband service using Hybrid Fibre-Coaxial (HFC) technology, which combines fibre-optic and coaxial cables to provide high-speed internet access.
Here, we explain the different infrastructure components used to deliver cable broadband:
Core fibre network
Virgin Media’s broadband service relies on a core network of high-capacity fibre-optic cables that connect data centres, regional hubs, and local street cabinets.
Virgin’s street cabinets are located in local areas and serve as distribution points to connect nearby homes and businesses.
Coaxial cable for final mile
From the street cabinet, coaxial cables carry internet data to individual homes and businesses.
These high-performance coaxial cables can carry high-bandwidth signals over relatively short distances without significant signal loss.
Virgin Media Hub (router)
The coaxial cable connects to a Virgin Media Hub (a business broadband router) inside a home or commercial property.
The router provides a Wi-Fi signal and an Ethernet connection point for devices within the property.
Cable broadband vs other broadband types
In this section, we’ll compare cable broadband technology and performance to other types of fibre optic business broadband.
Cable vs SoGEA
SoGEA broadband is the part-fibre (FTTC) product offered by Openreach. It uses a copper business phone line cable to deliver internet to a router.
The copper phone line cable used by SoGEA supports a maximum download speed of 80Mbps. This is more than ten times slower than the 1.1Gbps download speeds cable business broadband can deliver.
Find out more in our guide to SoGEA business broadband.
Cable vs full fibre
Full fibre business broadband is a connection offered by Openreach, Hyperoptic, and CityFibre.
Full fibre uses a fibre-optic cable between the local street cabinet and the properties using the service.
Fibre-optic cables deliver superior performance to coaxial cables, with less signal loss and lower latency.
Full fibre offers download speeds of up to 1.6 Gbps, approximately 50% faster than cable.
Cable vs leased line
A leased line business broadband service uses a dedicated fibre-optic cable between a local exchange and the property receiving the broadband service.
The key difference between a leased line and other types of fibre-optic broadband mentioned above is that the fibre-optic cable between the local cabinet and exchange is not shared with other customers.
This means a leased line offers an uncontended broadband service, delivering consistent high speeds of up to 10Gbps.
Leased line broadband providers include Virgin, BT, Hyperoptic, and TalkTalk business broadband.
Cable broadband plans and speed tiers
Broadband plans on the cable network are exclusively offered by Virgin Media. The following table shows the home and business broadband speed tiers and plans available from Virgin on the cable network:
| Cable Plan Name | Customer Type | Average Speeds |
|---|---|---|
| M125 Fibre | Household | 132Mbps download, 20Mbps upload |
| M250 Fibre | Household | 264Mbps download, 25Mbps upload |
| M350 Fibre | Household | 362Mbps download, 35Mbps upload |
| M500 Fibre | Household | 516Mbps download, 52Mbps upload |
| Gig1 | Household | 1,130Mbps download, 104Mbps upload |
| Voom 200 | Business | 200Mbps download, 20Mbps upload |
| Voom 400 | Business | 400Mbps download, 40Mbps upload |
| Voom 600 | Business | 600Mbps download, 60Mbps upload |
| Voom Gig1 | Business | 1,000Mbps download, 100Mbps upload |
Virgin Media frequently runs time-limited offers. For the latest home and business broadband prices, visit the Virgin Media website.
Cable broadband coverage and availability
The Virgin Media cable network is Britain’s second most extensive fibre network after Openreach.
In this section, we’ll explain the coverage and availability of cable broadband, including network expansion plans.
Where is cable broadband available?
Virgin Media cable is available in most urban locations across England, Scotland, and Wales, and reaches approximately 56% of UK properties.
Learn more about broadband service availability on our business broadband availability page.
Cable broadband location checker
To determine whether cable broadband is available at your location, simply enter your postcode into Virgin Media’s postcode checker tool.
If you want to explore all the broadband options available at your location, use our business broadband comparison service. Our broadband experts will talk you through all the choices and give you their best recommendations.
Cable broadband expansion
Virgin Media has ceased expanding its cable network and has shifted its focus to full fibre.
While cable broadband has remained competitive with full fibre until now, it is widely recognised that full fibre is a superior technology for connectivity.
Virgin Media is extending its reach through a partnership with the Nexfibre network, which offers a full fibre connection type.
The Nexfibre network aims to make full fibre broadband available to 5 million premises by the end of 2026.
What do businesses use cable broadband for?
Companies of all sizes use cable broadband connections. Here are some of the most common use cases:
- Small businesses – Small business broadband customers frequently use cable broadband as their primary connection. A basic cable plan is sufficient to run essential business tools like business VoIP phone systems.
- Medium businesses – The Gig1 plan can provide enough bandwidth for medium-sized businesses, supporting multiple users accessing the internet simultaneously.
- Redundancy – Cable broadband is a strong business broadband redundancy option, as it does not rely on the Openreach network used by most business broadband providers.
- Load balancing – Businesses often add cable broadband to their network load balancing setup to increase available bandwidth.
What are the advantages of cable broadband?
Virgin Media’s cable broadband presents several key advantages over other fibre networks:
- Wide coverage – Virgin’s cable broadband is available to 16 million properties and in areas where Openreach coverage is limited, it can be the only viable option for gigabit broadband.
- Gigabit speeds – Cable broadband is among the best-performing business broadband connection types
- Bundled services – Virgin Media offers commercial broadband bundled with business phone lines and O2 business SIM only deals.
- Affordability – Virgin Media business broadband prices are competitive and comparable to alternative connection types.
What are the disadvantages of cable broadband?
If you are considering cable broadband, it’s important to be aware of the following potential drawbacks:
- Limited rural availability – Like other fibre networks, Virgin’s cable broadband is unavailable in most rural areas. For many in these locations, alternatives such as wireless leased line or satellite business broadband may be more viable options.
- Higher latency – Despite its gigabit capabilities, cable broadband cannot match the low latencies other full fibre connections offer.
- Long contracts – Switching business broadband to a cable connection currently requires a minimum contract term of 24 months.
- New installation – Choosing cable for the first time requires a new broadband installation, which can take several weeks to arrange. Visit our business broadband installation page for more information.

