Business satellite internet
Save your business thousands with our satellite deals
Just enter your business postcode…
Save your business thousands with our satellite deals
Just enter your business postcode…
Start saving now
Looking for a broadband solution that works anywhere in the UK? Business satellite broadband offers reliable internet connectivity, even in remote areas where traditional broadband falls short.
Use our service to compare the best deals and connect easily.

Enter your postcode and a few key details about the broadband requirements in our smart form.

Get personalised advice to help you choose the right package for your business.

Enjoy fast installation and start benefiting from reliable, high-speed business satellite internet.
Satellite internet has transformed connectivity, providing a dependable solution for businesses in remote and underserved areas. It bridges the gap where traditional broadband infrastructure falls short, ensuring businesses stay connected regardless of location.
Below are the key benefits of satellite internet for businesses:
Satellite internet can reach rural and remote areas where traditional broadband services are unavailable. It’s an essential service for operations in locations too remote for other forms of internet access.

Satellite internet doesn’t require extensive infrastructure such as cables or phone lines to be installed. Typically, you sign up for the service through a satellite broadband provider, receive your satellite dish by post, set it up in minutes, and you’re ready to go.

Advancements in satellite technology, particularly with Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites, have dramatically improved speeds and reliability. Services like Starlink now rival 5G business broadband and business fibre optic broadband in performance, making satellite internet a viable option for modern business needs.
The UK offers several satellite business broadband providers catering to various needs. These providers are satellite network operators or third-party resellers that bundle additional services. Here’s an overview of the leading satelitte business broadband providers:

Starlink, operated by SpaceX, offers high-speed, low-latency broadband through a large Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellation. It’s available across mainland UK and maritime borders, providing a reliable service for businesses in remote areas.

FreedomSat delivers satellite broadband using KA-SAT and HYLAS 1 GEO satellites, offering 25–50 Mbps download speeds. With flexible plans and data caps ranging from 10 to 100 GB, they cater to businesses in rural or remote areas needing reliable internet access.

Brdy offers satellite broadband using a mix of LEO and GEO networks, including Starlink, OneWeb, and Eutelsat. They provide tailored solutions for industries like healthcare, agriculture, retail, and offshore energy, focusing on delivering reliable service for diverse business needs.

Bigblu is a third-party provider offering satellite broadband via Eutelsat’s GEO satellites. They offer several packages for rural businesses, with pricing available upon enquiry, making them a good choice for businesses needing tailored satellite broadband services.

BT business broadband offers satellite internet in partnership with OneWeb and Eutelsat, providing reliable internet services for businesses in remote or challenging locations. Their services integrate seamlessly with BT’s wider business broadband deals.
Satellite broadband comes in three main types, determined by the orbit of the satellite network your business connects to. Each orbit has unique features affecting speed, latency, and coverage. Here’s a quick breakdown:
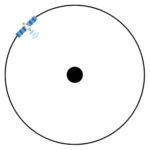
GEO satellites orbit 35,786 km above the equator, staying fixed relative to a point on Earth. They provide wide coverage per satellite, making them ideal for broadcasting and broad-area connectivity. Speeds range from 10–100 Mbps, but latency is higher at 600–800 ms due to the long signal travel distance.
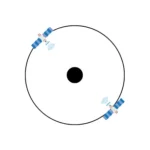
MEO satellites operate at 2,000–35,786 km altitudes, balancing speed and latency. With speeds of 25–150 Mbps and latency of 150–250 ms, they require fewer satellites than LEO for continuous coverage, making them suitable for regional broadband services.
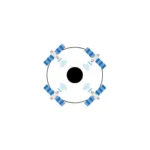
LEO satellites orbit at altitudes of 160–2,000 km, providing the fastest speeds (100–200+ Mbps) and lowest latency (20–60 ms). Their proximity to Earth enables high performance but requires a large constellation of satellites to ensure consistent global coverage.
Satellite broadband is a type of internet service that utilises a network of satellites to provide broadband connectivity to users anywhere in the UK. The service requires businesses to install an antenna dish with uninterrupted exposure to the sky.
It is disrupting existing broadband markets by offering high-performance broadband to rural or remote areas that continue to lack access to traditional forms of broadband, such as fibre optic business broadband and 5G.
This is due to advancements in internet satellite technology and increasing competition from new entrants like Starlink and OneWeb.
All satellite internet providers operate on the same principles:
Satellite broadband offers incredible benefits, especially for businesses in remote locations, but it’s not without challenges. Understanding these common issues can help you decide if satellite broadband is the right choice for your business.

Satellite internet typically experiences higher latency than terrestrial broadband due to the long distance signals must travel between the Earth and the satellite. While modern technologies like LEO satellites reduce this issue, latency can still affect VoIP call quality and other business-critical applications.

Weather conditions like heavy rain, snow, or dense cloud cover can interfere with satellite signals. Obstructions like tall trees, buildings, or even aeroplanes can also affect performance, making clear line-of-sight crucial for reliability.
Many business satellite broadband plans have restrictive data limits, which can challenge businesses with high bandwidth needs, such as video conferencing, cloud computing, or large file transfers. Exceeding data caps can result in slower speeds or additional charges.

Some providers use NAT-based IPs (Network Address Translation), where multiple devices share a single IP address. This can cause issues with applications like VPNs or VoIP, which often require unique IPs for optimal performance.

Business satellite broadband is generally more expensive than full fibre business broadband or SoGEA business broadband options due to higher infrastructure and operational costs. Businesses must account for higher business broadband prices and upfront costs for equipment like satellite dishes and modems.

The satellite broadband market is still developing, with relatively few providers compared to traditional broadband. This limited competition can make finding flexible packages or tailored services harder, though the market is expanding with new players and technologies.
The cost of business satellite broadband is typically composed of the following:
The most basic GEO satellite broadband service can start at as little as £24.99 with Bigblu, while a premium LEO plan from Starlink could cost your business up to £360 per month. The cost will depend on the satellite network being used, data and speed limits.
For example, Starlink’s service costs depend entirely on your data requirements, with business broadband speed remaining fixed for all plans:
| Service Type | Cost |
|---|---|
| 40 GB limit | £96 per month |
| 1TB limit | £180 per month |
| 2TB limit | £360 per month |
| Other Charges | £200 single time activation charge per connection |
A satellite dish and a modem are core requirements of any satellite broadband deal. Some providers will charge a monthly fee for rental, while others will let you outright purchase it. Here’s the cost for purchase or rental for their hardware:
| Hardware Type | High-performance | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Use Case | More resilient, can connect to more satellites, and higher bandwidth | Designed for non-critical uses or small business broadband customers |
| Purchase Cost | £2,470 | £570 |
| Rental Cost | N/A | £100 per month |
Most providers will ask for a one-time activation fee to capitalise on the onboarding of new users or pay their customer acquisition costs.
Typically, businesses receive the hardware by post and do the installation themselves, but others with custom requirements or who simply want to guarantee a proper installation or meet insurance criteria will also pay for a one-time installation fee for an expert to come and do it.
Third-party providers typically offer add-ons like static IPs, flexible contracts, and insurance with their plans, which comes at an additional price.
Satellite broadband has come a long way in delivering reliable connectivity for businesses, even in remote locations. Its performance depends on the type of satellite network, with factors like speed, latency, and consistency varying across different providers and technologies. Here’s what you need to know:
The speeds of satellite broadband vary depending on the satellite network in use, with those in lower orbits able to support higher speeds comparable to fibre broadband.
Satellite internet has higher latency than traditional broadband due to the long distance that signals must travel from the Earth to the satellite and back.
Here is a list of the typical speeds and latencies of various internet satellite networks currently serving the UK:
| Satellite Network | Type | Download Speeds (Mbps) | Latency (ms) | Operating since |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Starlink | LEO | 25-220 | 25-60 | 2020 |
| OneWeb | LEO | <150 | <40 | 2022 |
| Avanti HYLAS | GEO | 10 | 500 - 800 | 2010 |
| Viasat KA-SAT | GEO | <50 | 600 - 800 | 2011 |
| Eutelsat KONNECT VHTS | GEO | <100 | 600 - 700 | 2023 |
| Viasat-3 (Coming Soon) | GEO | <100 | <800 | Expected 2024-25 |
Satellite internet has higher latency than traditional broadband due to the long distance that signals must travel from the Earth to the satellite and back.
This is especially true with GEO satellite broadband where signals must travel at least 70,000km before reaching their destination.
However, the new generation of LEO satellites, which orbit the closest to Earth, have low enough latencies for contemporary internet uses like video conferencing and business VoIP phone systems.
The table below shows how speeds and latencies compare to traditional broadband technologies:
| Technology | Typical speeds (Mbps) | Typical latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| Full fibre business broadband | 70 - 1000+ | 5 - 10ms |
| SoGEA | 30 - 70 | 10 - 15ms |
| Cable (Virgin) | 100 - 1000+ | 10 - 20ms |
| 5G | 50 - 1000 | 5 - 70ms |
| 4G | 10 - 50 | 30-50ms |
| LEO satellites, Starlink, OneWeb | <400 | 20-70ms |
| GEO satellites | <100 | 500-1000ms |
Choosing the right customer support is key to a smooth transition to satellite broadband. Here’s how different providers and services support your business needs:
Providers like FreedomSat and Relialink offer hands-on assistance, including phone and email support, billing portals, and data usage monitoring. These options are ideal for businesses that value personalised human support for troubleshooting and account management.

Starlink provides comprehensive automated tools through its website and app, enabling users to monitor performance, data usage, and billing with ease. While efficient, this model may not always suit businesses requiring direct human assistance for complex IT needs
Our experts offer a fully managed service to ensure a smooth transition to satellite broadband. From seamless installations, round-the-clock support, and integration with your existing technologies, we handle every step to deliver optimal connectivity for your business. Let us help you start your satellite broadband journey with ease; simply enter your postcode above.
Getting satellite broadband for your business is simple. Follow these three steps to get started:

Provide your business location and how many users you have. This helps identify the best satellite broadband options available for your specific requirements.

Discuss your needs with our business satellite broadband experts, who can guide you through the available plans, providers, and pricing to find the perfect match for your business.

Once you’ve chosen a provider, they’ll send you a satellite dish and modem. Follow the setup instructions or arrange professional installation to get your business connected quickly.
Satellite broadband provides a scalable solution for businesses, making it ideal for organisations in remote areas or those without access to leased line business broadband or other connectivity options. Here’s how it supports growth:

Providers are investing in expanding satellite constellations and launching new technologies like Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) systems. These innovations mean satellite networks keep pace and actively enhance capacity to meet future business demands.

Satellite broadband doesn’t rely on local infrastructure, making it ideal for businesses expanding to multiple or remote sites. New locations can be connected quickly without waiting for fibre or cable installation, supporting seamless scalability.

Business satellite broadband provides a scalable, temporary solution for businesses in transitional stages. Whether expanding operations or waiting for a wireless leased line installation, satellite ensures you stay connected during growth and change.
While both satellite and 5G broadband are wireless technologies, they are delivered through different means. Satellite broadband is provided via satellites in orbit, whereas 5G (along with other mobile broadband technologies like 4G, 3G, and LTE) is delivered through terrestrial cellular antennas.
5G offers faster speeds and lower latency but is only available within proximity to these antennas. In contrast, satellite broadband, though slower and with higher latency, offers ubiquitous coverage, making it accessible from virtually anywhere.